| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
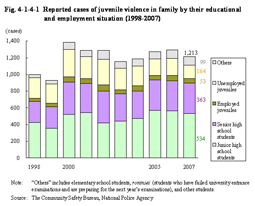
1 Family violence The number of reported cases of juvenile violence in family declined after hitting a peak at 1,397 cases in 1983, but increased significantly in 2000 and has been over 1,000 cases ever since. The number decreased by 6.3% from the previous year to 1,213 cases in 2007. Junior high school students constitute the highest proportion, by educational and employment situation in each year, and in 2007, they accounted for 44.0% (534 cases) of total juvenile family violence cases (Source: The Community Safety Bureau, National Police Agency). Fig. 4-1-4-1 Reported cases of juvenile violence in family by their educational and employment situation (1998–2007) As the targets of family violence in 2007, mothers were the most frequent, accounting for 730 cases (60.2%), followed by material objects (family property, etc.) for 162 cases (13.4%), relatives in the same household for 137 cases (11.3%), siblings for 86 cases (7.1%), fathers for 84 cases (6.9%), and others for 14 cases (1.2%) (Source: The Community Safety Bureau, National Police Agency). |