4 Criminal trials
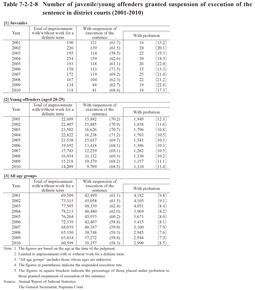
Table 7-2-2-8 shows the number of juveniles/young offenders granted suspension of execution of the sentence in district courts over the last 10 years. The suspended execution rate of juveniles was higher than that of the total basically every year and that of young offenders consistently around 10 points higher than that of the total. Of those granted suspension of execution of the sentence the percentage of those placed under probation was higher with juveniles than with young offenders every year, while those of juveniles and young offenders were both higher than that of the total (see Table 3-2-2-2).
Table 7-2-2-8 Number of juvenile/young offenders granted suspension of execution of the sentence in district courts (2001-2010)
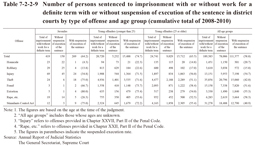
Table 7-2-2-9 shows the number of persons sentenced to imprisonment for a definite term, with or without suspension of execution of the sentence, in district courts in the cumulative total for 2008-2010 by type of offense and by age group.
Examining the percent distribution of juveniles by type of offense revealed that the proportion of serious offenses such as homicide (5.5%) and robbery (6.9%) was relatively high, influenced by family court trend in referring these cases to public prosecutors, and most of the juveniles who committed these offenses were sentenced to imprisonment without suspension of execution of the sentence.
With young offenders, the proportion of theft, Stimulants Control Act violations, injury, and fraud was high. The percent distribution by type of offense of young offenders aged 25 or older generally reflected the same trends as that of the total for all age groups, but that of young offenders younger than 25 was somewhat different, with the proportion of theft being higher (23.8% with those younger than 25 and 18.1% with those aged 25 or older) and that of Stimulants Control Act violations lower (11.2% with those younger than 25 and 16.8% with those aged 25 or older).
Examining the suspended execution rate of young offenders by type of offense revealed that the suspended execution rate for injury, theft, fraud, extortion, and Stimulants Control Act violations was all extremely high at over 70% with young offenders younger than 25, although they all remained within the range of 50-60% with young offenders aged 25 or older.
Table 7-2-2-9 Number of persons sentenced to imprisonment with or without work for a definite term with or without suspension of execution of the sentence in district courts by type of offense and age group (cumulative total of 2008-2010)