| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
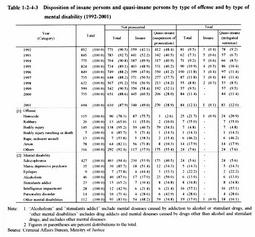
2 Type of offense which insane persons or quasi-insane persons committed and type of mental disability from which they suffered Table 1-2-4-3 shows the trends in (a) the number of suspects who were not prosecuted by public prosecutors offices on the grounds of being insane or quasi-insane, (b) the number of persons who were found not-guilty on the grounds of being insane, or the number of persons whose punishment was mitigated on the grounds of being quasi-insane, in the first instance over the last decade from 1992 to 2001, and (c) the disposition by type of offense and type of mental disability in 2001. In 2001, 406 out of 694 insane and quasi-insane persons were involuntarily admitted to mental hospitals, and 65 were sentenced to imprisonment without suspended sentence or taken into custody. Regarding the 340 persons who were not prosecuted on the grounds of being insane in 2001, by type of offense, homicide (87) had the largest share, followed by bodily injury (59), and arson (56), and by type of mental disability, schizophrenia had the largest share, numbering 230 persons (see Appendix 1-11 and 1-12 ).
Fig. 1-2-4-1 Trends in the number of mentally disabled persons, etc. cleared for penal code offenses (1992-2001) Fig. 1-2-4-2 Numbers of mentally disabled persons, etc. cleared for penal code offenses by type of offense (2001) Table 1-2-4-3 Disposition of insane persons and quasi-insane persons by type of offense and by type of mental disability (1992-2001) Additionally, as for the 270 persons who were not prosecuted on the grounds of being quasi-insane in 2001 by type of offense, bodily injury (79) had the largest share, and on the other hand, by type of mental disability, schizophrenia (173) had the largest share, followed by alcoholism (23).As for the 83 persons who were treated as quasi-insane persons and mitigated the sentence in the first instance in 2001, by type of offense, homicide (24) had the largest share, and then, by type of mental disability, schizophrenia (24) had the largest share, followed by intelligence impairment (16). |