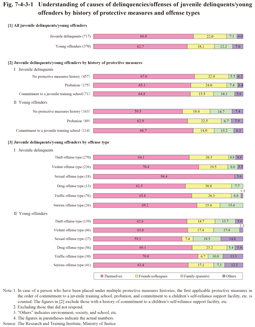
1 Understanding of the causes of delinquencies/offenses
Fig. 7-4-3-1 shows the understanding of the causes of delinquencies/offenses (answers to the question of “what do you think causes youth to commit delinquencies/offenses”). First, examining the answers of all the juvenile delinquents and young offenders (Fig. 7-4-3-1 [1]) revealed that over 60% regarded “themselves” as the cause (66.8% with juvenile delinquents and 62.7% with young offenders), followed by friends/colleagues (22.0% and 18.1% (id.)) and families (7.1% and 12.2% (id.)). When compared with the 2005 survey the proportion of those that regarded themselves as the cause has risen by approximately 10 points and that of those who regarded friend relationships as the cause has declined by approximately 10 points in this survey. With young offenders the proportion of those that regarded their families as the cause was higher than with juvenile delinquents.
Fig. 7-4-3-1 [2] shows understanding of the causes of delinquencies/offenses of juvenile delinquents/young offenders by history of protective measures. With both juvenile delinquents and young offenders in the respective protective measure history categories generally over 60% regarded “themselves” as the cause. The proportion of those that regarded their “families” as the cause was remarkably high with juvenile delinquents with a history of commitment to a juvenile training school (14.1%) when compared to juvenile delinquents without a history of protective measures. In addition, examining the answers of those with a history of commitment to a children’s self-reliance support facility, etc. (including those that also had other protective measure histories) revealed that the proportion of those that regarded their “families” as the cause was higher (26.1% with juvenile delinquents and 20.8% with young offenders) than with those with a history of commitment to a juvenile training school and that of those who regarded “friends/colleagues” as the cause lower (8.7% and 8.3% (id.)). This indicates that problems within their families accounted for a large part of their understanding with the causes of the delinquencies/offenses with these juvenile delinquents/young people than with others.
Fig. 7-4-3-1 [3] shows understanding of the causes of delinquencies/offenses of juvenile delinquents/young offenders by type of delinquency/offense (based on the classification of Section 3 of the previous chapter for both juvenile delinquents and young offenders) for which they were admitted to juvenile classification homes/penal institutions of concern with this survey. Across all types those that regarded “themselves” as the cause accounted for the largest in number. With juvenile delinquents belonging to the sexual offense type the proportion of those that regarded “themselves” as the cause was extremely high (94.4%). In addition, the proportion of those that regarded their “friends/colleagues” as the cause was relatively high with those belonging to the drug (30.8%), theft (26.3%), and traffic (26.3%) offense types. With young offenders the proportion of those that regarded their “friends/colleagues” as the cause was particularly high with those belonging to the drug offense type (23.2%), but low with those belonging to the sexual (7.4%) and traffic (6.7%) offense types. Associating with delinquent friends was pointed out as a risk factor to repeat offenses in connection with the characteristics of the respective offense types in the previous chapter. The same trends were observed with the attitudes of juvenile delinquents/young offenders.
Fig. 7-4-3-1 Understanding of causes of delinquencies/offenses of juvenile delinquents/young offenders by history of protective measures and offense types