8 Attitudes toward community
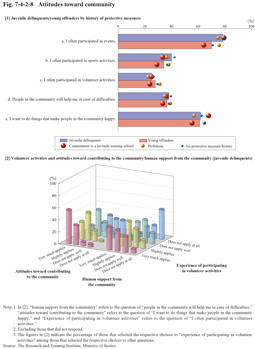
Fig. 7-4-2-8 [1] shows the attitudes toward their community. The level of participation in their community of juvenile delinquents and that of young offenders showed similar trends, and a relatively high percentage of them answered that they had experienced participating in community festivals and other events (78.4% with juvenile delinquents and 69.9% with young offenders), but only a low percentage of them had experienced participating in sports activities (39.9% and 34.1% (id.)) and volunteer activities (24.9% and 27.7% (id.)). In addition, while only approximately 40% showed a sense of trust in human support from their community with affirmative answers to “people in the community will help me in case of difficulties” (38.0% and 36.6% (id.)), approximately 60% showed their willingness to contribute to their community with affirmative answers to “I want to do things that make people in the community happy” (61.7% and 61.0% (id.)). With young offenders with a history of commitment to a children’s self-reliance support facility, etc., however, the percentage of those that had experienced participating in sports activities (8.3%) and volunteer activities (8.3%) in their community was extremely low, while the percentage of those that showed a sense of trust in human support from their community (16.7%) and a willingness to contribute to their community (33.3%) was also extremely low with both, being about half of that with all young offenders. This indicates that they were weakly connected to their community, and therefore had little sense of trust in human support from their community and are not very much willing to contribute to their community (no such trends were observed with juvenile delinquents with the said history).
Fig. 7-4-2-8 [2] shows the answers concerning human support from their community (item d.) and attitudes toward contributing to their community (item e.) by the answers concerning experience of participating in volunteer activities (item c.) with juvenile delinquents. Those with more experience of participating in volunteer activities tend to have more of a sense of trust in human support from their community and a stronger willingness to contribute to their community (similar trends were observed with young offenders).
Fig. 7-4-2-8 Attitudes toward community