| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
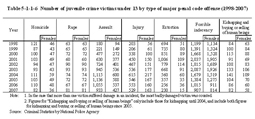
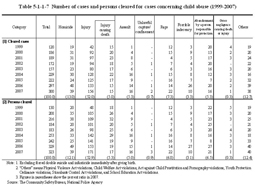
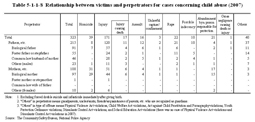
6 Juvenile crime victims Table 5-1-1-6 shows the number of juvenile crime victims who were under 13 years of age, by type of major penal code offense over the last 10 years. Table 5-1-1-6 Number of juvenile crime victims under 13 by type of major penal code offense (1998–2007) The number of juvenile crime victims under 13 has increased significantly for assault and injury from 1998. The female rate among the total number of victims, for each offense (excluding rape) in 2007, was the highest for forcible indecency (89.7%), followed by kidnapping and buying or selling of human beings (70.7%), and assault (45.8%).(2) Child abuse The Act on Prevention of Child Abuse (Act No. 82 of 2000) covers abusive acts on children under 18. The Act clarifies the definition of child abuse and specifies matters concerning the prevention and detection of child abuse and measures to be taken after any child abuse is detected. Table 5-1-1-7 shows the number of cases and persons cleared for abusive acts specified by this Act as penal code offenses, etc. (hereinafter such cases shall be referred to as “cases concerning child abuse” in this section), over the last nine years. Table 5-1-1-7 Number of cases and persons cleared for cases concerning child abuse (1999–2007) Table 5-1-1-8 shows the relationship between victims and perpetrators of cases concerning child abuse in 2007.Fathers, etc. took up the largest proportion with 215 persons (66.6%) among overall persons cleared for cases concerning child abuse, but with regard to homicide and abandonment by a person responsible for protection, the percent ratio of cases by mothers, etc. was high with 31 persons (79.5%) and 17 persons (81.0%), respectively. Table 5-1-1-8 Relationship between victims and perpetrators for cases concerning child abuse (2007) |