| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
3 Sentencing
The criminal justice system functions in preventing offenses by dispensing appropriate sentences to offenders. Realizing appropriate sentences contributes to the prevention of recidivism (see Part 7, Chapter 5, Section 1).
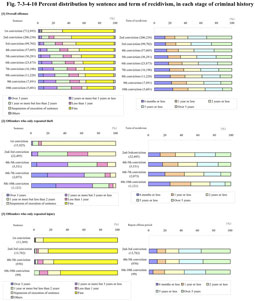
In this subsection, the relationship between recidivism and sentencing is examined. The overall offenses with the convictions, and respectively on theft, injury and Stimulants Control Act violations, whose numbers are large in recorded convictions, and with which recidivism prevention measures are important, were all examined. In order to reveal the changes in sentencing as offenders accumulate the number of convictions, from first to second, and so on, Fig. 7-3-4-10 shows the percent distribution by sentence and term of recidivism, in each stage of their criminal history, with regard to the overall offenses, persons who only repeated theft, persons who only repeated injury and persons who only repeated Stimulants Control Act violations, based on the 700,000 Non-Repeat and Repeat Offenders' Recorded Convictions. Fig. 7-3-4-10 Percent distribution by sentence and term of recidivism, in each stage of criminal history In each case, the sentence becomes severer as their number of convictions increases.On the other hand, the term of recidivism tends to become shorter as their number of convictions increases, with regard to the overall offenses, with persons who only repeated theft, and persons who only repeated Stimulants Control Act violations. As the number of convictions increases, the actual number of persons decreases markedly, as is shown in parentheses. However, on the other hand, even if they are given heavier penalties, as far as theft and Stimulants Control Act violations are concerned, it is also a fact that a certain number of persons exist who repeat the same offense, showing a tendency to make their terms of recidivism shorter. In regard to those who only repeated injury, as this is thought to be due to the presence of many minor cases, fines accounted for about 69% even for the 6th-10th conviction, and no particular trend can be observed in their terms of recidivism by the stage of their criminal history. |