| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
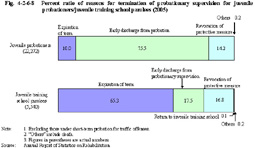
3 Termination of probationary supervision (1) Reasons for termination Fig. 4-2-6-8 shows the percent ratio of reasons for termination of probationary supervision for juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees in 2005.
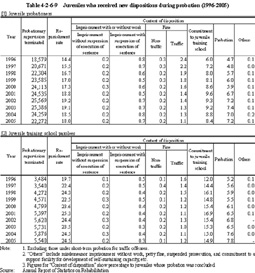
As for juvenile probationers, the percentage of those who were granted early discharge from probation has been around 75% since 1995. As for juvenile training school parolees, the percentage of those who were granted early discharge from parole (those whose parole was terminated earlier by a request from the director of a probation office or a decision by a Regional Parole Board) has been between 17% and 20% since 1996, and the percentage of those who completed the term has been around 65%.The percentage of those who were returned to a juvenile training school (those who were returned to a juvenile training school by a decision of a family court in response to a proposal from the director of a probation office and a request from a Regional Parole Board) or those who received revocation of protective measures (those whose former treatment was revoked because they were placed under new treatment due to repeating delinquency or offense) has been between 15% and 18% since 1998. There have been no significant changes in these percentages. Fig. 4-2-6-8 Percent ratio of reasons for termination of probationary supervision for juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees (2005) In 2005, good-conduct measures (temporary suspension of probation) were taken for 43 juvenile probationers, and notification to family court was implemented for 19 juvenile probationers due to new pre-delinquency (Source: The Rehabilitation Bureau, Ministry of Justice).(2) Percentage of those who received new dispositions Table 4-2-6-9 shows the percentage of those juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees who were placed under new protective measures (excluding return to juvenile training schools) or received criminal dispositions due to repeating offenses or delinquent acts during their probation among those whose probation was concluded, over the last 10 years.
Table 4-2-6-9 Juveniles who received new dispositions during probation (1996-2005) |