| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
2 Treatment (1) Classified treatment system As of December 31, 2005, the percentage of "Class A" juveniles (the rate of those who were considered to be difficult to treat; see Part 2, Chapter 5, Section 2, 2 (1)) was 4.4% for juvenile probationers and 18.2% for juvenile training school parolees. The percentage of "Class A" juvenile probationers and that of "Class A" juvenile training school parolees has been on a declining trend since 1996 and 1993, respectively. The higher percentage of "Class A" juvenile training school parolees indicates that juvenile training school parolees were more likely to have problems that might hinder their rehabilitation.
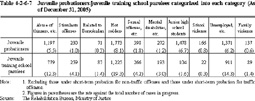
(2) Categorized treatment system Table 4-2-6-7 shows the situation of juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees categorized into each category according to their characteristic problems (see Part 2, Chapter 5, Section 2, 2 (2)) as of December 31, 2005.
Table 4-2-6-7 Juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees categorized into each category (As of December 31, 2005) (3) Social participation activities In probationary supervision, juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees are encouraged to participate in nursing care and volunteer work at welfare facilities, environment beautification activities such as park cleaning, etc., on-site training such as pottery classes and cooking classes, farm work, sport activities, and recreational activities, etc. in order to foster a social nature in juveniles and enhance their capacity for adaptability to society. Such social participation activities were first started as one of the methods to implement short-term probation for non-traffic offenses, and then came to be applied widely to all juvenile probationers/parolees.
In FY2005, social participation activities were implemented 430 times, at 298 sites with the participation of 1,520 persons (including 193 guardians). Activities that were implemented most frequently were "participation in nursing care activities and volunteer activities for the aged, etc. (162 times)", "participation in creative activities, on-site training, and various classes, etc. (100 times)", and "participation in cleaning and environmental beautification activities (75 times)" (Source: The Rehabilitation Bureau, Ministry of Justice). Social participation activities (Volunteer activities at a special elderly nursing home) |