| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
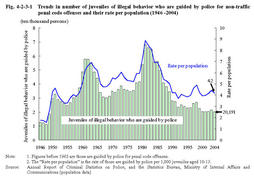
Fig.4-2-3-1 shows the number of juveniles of illegal behavior who are guided by police for non-traffic penal code offenses and their rate per population(the rate of those are guided by police per1,000juveniles aged10-13;hereinafter the same in this Section),since1946.
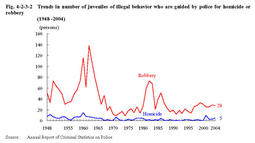
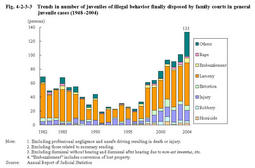
Fig.4-2-3-1 Trends in number of juveniles of illegal behavior who are guided by police for non-traffic penal code offenses and their rate per population(1946-2004) Fig.4-2-3-2 shows the number of juveniles of illegal behavior who are guided by police for homicide or robbery since1948(see Appendix4-6 for other major type of offense).Fig.4-2-3-2 Trends in number of juveniles of illegal behavior who are guided by police for homicide or robbery(1948-2004) Fig.4-2-3-3 shows the number of juveniles of illegal behavior finally disposed by family courts(excluding those who were referred to family courts by summary procedure)in general juvenile cases(excluding professional negligence and unsafe driving resulting in death or injury)since1982.By type of delinquency,larceny accounted for the largest share each year,and was45.9%in2004,followed by injury at11.3%. Fig.4-2-3-3 Trends in number of juveniles of illegal behavior finally disposed by family courts in general juvenile cases(1948-2004) |