| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
1 Trends in high-technology related offenses and disposition by public prosecutors offices and courts High-technology related offenses are those offenses that are committed by misusing computer technology and telecommunication technology.
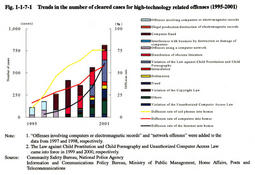
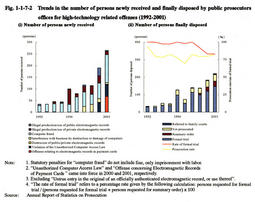
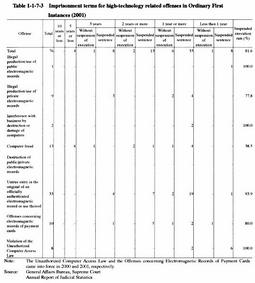
These offenses are roughly categorized into the following 3 groups: (a) offenses involving computers or electromagnetic records ( computer offenses in the narrow sense); (b) offenses using a computer network ( network offenses ); and (c) violation of the Unauthorized Computer Access Law ( Unauthorized computer accessing acts , etc). Category (a) includes the illegal production, use, and willful injury of various electromagnetic records, business interference through destruction or damage of computers, and computer fraud. Category (b) includes fraud using the Internet and the distribution of child pornography (Violations of the Law against Child Prostitution and Child Pornography). Fig. 1-1-7-1 shows the trends in the number of cases cleared for high-technology related offenses and the diffusion rate of the Internet and computers into homes over the last 7 years. Overall, the number of cases cleared for these offenses increased rapidly for a few years in proportion to the diffusion rate of the Internet and computers into homes, etc. (Source: Community Safety Bureau, National Police Agency). Fig. 1-1-7-2 shows the trends in the number of persons newly received and finally disposed by public prosecutors offices over the last decade for high-technology related offenses such as illegal production of electromagnetic records by type of offense. Over all, the number of persons newly received and disposed for high-technology related offenses has increased rapidly over the last decade, though there were some increases and decreases for each offense. As for high-technology related offenses, prosecution rates and rates of requesting formal trial generally exceeded 75%, marking a high percentage in comparison with other penal code offenses. Table 1-1-7-3 shows the term of imprisonment with labor given by ordinary first instances for high-technology related offenses in 2001. The suspended execution rate for those sentenced to imprisonment with labor for computer fraud was 38.5% in 2001. Fig. 1-1-7-1 Trends in the number of cleared cases for high-technology related offenses (1995-2001) Fig. 1-1-7-2 Trends in the number of persons newly received and finally disposed by public prosecutors offices for high-technology related offenses (1992-2001) Table 1-1-7-3 Imprisonment terms for high-technology related offenses in Ordinary First Instances (2001) |