Chapter 5 Cybercrime
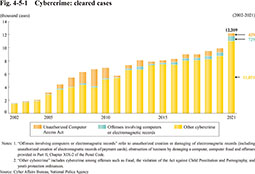
Fig. 4-5-1 shows the trend in the number of cleared cases of cybercrimes (violations of the Act on Prohibition of Unauthorized Computer Access (Act No. 128 of 1999), offenses involving computers or electromagnetic records, and other offenses using computer networks as vital tools of the crime).
Fig. 4-5-1 Cybercrime: cleared cases
Click here for the Excel file (Japanese)
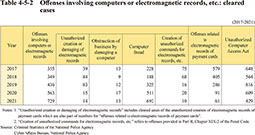
Table 4-5-2 shows the trend in the number of cleared cases for offenses involving computers or electromagnetic records (unauthorized creation or damaging of electromagnetic records, obstruction of business by damaging a computer, computer fraud, and creation of unauthorized commands for electromagnetic records, etc.), violation of the Act on Prohibition of Unauthorized Computer Access, etc.
Table 4-5-2 Offenses involving computers or electromagnetic records, etc.: cleared cases
Click here for the Excel file (Japanese)
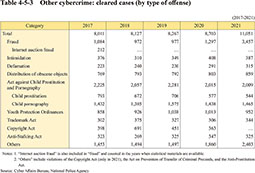
Table 4-5-3 shows the trend in the number of cleared cases for cybercrimes other than violations of the Act on Prohibition of Unauthorized Computer Access Act and offenses involving computers or electromagnetic records such as fraud, violations of the Act on Regulation and Punishment of Acts Relating to Child Prostitution and Child Pornography, and the Protection of Children (Act No. 52 of 1999; hereinafter referred to as “Act against Child Prostitution and Pornography”), and other offenses using computer networks as vital tools of the crime.
Table 4-5-3 Other cybercrime: cleared cases (by type of offense)