| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
5 Treatment of inmates in juvenile training schools (1) Lifein schools and assigned teacher system For effective correctional education,appropriate physical surroundings should be developed.
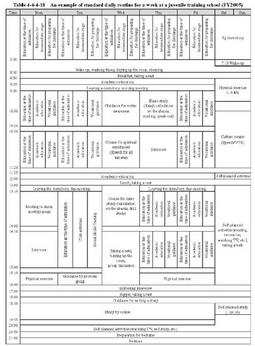
In particular,the residential environment has a significant meaning for the treatment of inmates.Room area,daylighting,air ventilation and other physical aspects of institutions should meet the standards of related laws.In addition to that,in recent years,the residential environment has been further improved by enhancing/securing vocational guidance rooms,academic education rooms,and broadcasting equipment,and painting facilities in light and tranquil colors,as well as installing heating equipment and modernizing sanitary equipment.Improvement of facilities has been underway in many juvenile training schools built between1955and1974. The front of a juvenile training school (Aichi Juvenile Training School) A room of a group dormitory(group room) The degree of confinement in each juvenile training school is different according to the characteristics and treatment stages of inmates.For example,buildings and rooms for special short-term treatment programs do not have bars and are unlocked.Life in schools differs according to treatment courses. Table4-4-4-18 illustrates a standard daily routine for a week for inmates placed under an academic education course(E1)at a certain male juvenile training school. Table4-4-4-18 An example of standard daily routine for a week at a juvenile training school(FY2005) A newly admitted juvenile usually spends one to two weeks after admission in a single room and then is placed into a group dormitory.As well,an individual assigned teacher is determined,who makes an individualized treatment plan and directly provides guidance for each inmate.An individual assigned teacher knows everything about each inmate's history of delinquency,family relations,and future career,etc.through interview and creation of his/her individualized treatment plan,and grasps the whole picture of implementation and achievement of the plan throughout the period from his/her admission to discharge.An individual assigned teacher is the person that each inmate asks first for advice on anything in life in school.Therefore,personal communication/contact with the individual assigned teacher is the base of life in school for each inmate. (2) Correctional education a. Living guidance Living guidance is implemented on the following issues:(i)problems related to his/her ways of thinking,attitude,and behavior that could lead to delinquency,(ii)problems related to his/her predisposition and emotions,(iii)spiritual enrichment,(iv)problems related to his/her basic living skills,law-abiding and self-disciplinary behavior,and interpersonal relationships,(v)problems in relationships with his/her family and friends,and(vi)preparation for career selection,life planning,and social rehabilitation.
Living guidance utilizes various methods,such as role lettering,role playing,interview guidance,and essay guidance,etc.Interview guidance and essay guidance is implemented at almost all juvenile training schools as a base of living guidance. Table4-4-4-19 shows the number of schools where following living guidance is implemented in addition to interview guidance and essay guidance. Table4-4-4-19 Number of schools where following living guidance is implemented(As of April1,2005) In juvenile training schools,guidance by problem group is also implemented,dividing inmates by their problems.Guidance through the above-mentioned methods is given to each group of juveniles who have the same problems in common.Table4-4-4-20 shows the number of schools where guidance by major problem group is implemented. Table4-4-4-20 Number of schools where guidance by major problem group is implemented(As of April1,2005) (a) Role lettering The role lettering method was developed in a juvenile training school in around1975.It is a method to make juveniles exchange imaginary roles with others through writing letters and leads them to self-insight.
How the role lettering method is used We will explain how the role lettering method is used at juvenile training schools through an example of writing a letter to"a mother".At the beginning,letters are often only superficial and safe,such as"I am sorry to make you worry."(inmate to mother),or"Reflect deeply on what you have done and rehabilitate yourself at the training school"(mother to inmate),or only hostile and antipathetic,such as"I don't want to see you again."(inmate to mother),or"I'm tired of taking care of you.I'm sorry but I can't be your guarantor."(mother to inmate).However,gradually,pent-up discontent and conflict come to be let out,such as"I was deeply shocked by your sudden divorce when I was an elementary school kid.I always felt very sad when I got back home from school and had to eat dinner all alone by myself."(inmate to mother),or"I'm sorry to have made you feel lonely.I worked very hard as I didn't want you and your brothers to have to worry about money.But not all children whose parents got divorced are led into delinquency.So please stop resorting to easy solutions."(mother to inmate).As a result,inmates can sort out their feelings and come to understand the feelings and position of the other side.Then they become aware of their own faults and selfishness seen from the other side. The role lettering method is also used as guidance to arouse repentance in inmates by making them write letters to their victims or victims'families.The role lettering method is considered to be very effective also in prompting inmates to feel physical and mental pains that crime victims and victims'families have gone through,and their anger toward inmates. (b) Role playing The role playing method,in which an inmate is made to play an imaginary role in a certain arranged scene,is now often used in the Social Skills Training(SST),training to improve an inmate's ability for interpersonal behavior.
How the SST is implemented The SST is implemented at juvenile training schools as follows; (i)Arrangement of a scene to solve a problem For example,inmates are trained how to act in a situation in which they see their former delinquent company and are asked to go to eat out together. (ii)Preliminary practice role play An inmate is made to play a role,under the instruction"Do what you always do".(iii)Indication of points to be improved Other inmates who watched the play are made to point out good points and further make comments for improvement. (iv)Model role play Other inmates who watched the play are made to pursue a new role play considering the improvements suggested in the above(iii). (v)New behavior role play The inmate(ii)is made to practice the model role play(iv).The process after(iii)is repeated. Through this repeated training of role play in the SST,inmates can have experience with which they can also build smooth interpersonal relationships with people around them and can display appropriate behavior even in a critical situation.Such experience gives them confidence,and as a result,expands the range of their behavior and enhances their abilities for solving problems. (c) Interview guidance Interview guidance aims to solve inmates'problems by solving interpersonal troubles among them and improving their relations with their guardians,removing their anxiety in making a decision on their careers after discharge(going to school or working,etc.),and stabilizing their emotions by relieving them from stresses of life in juvenile training schools.Interview guidance is in principle implemented one on one between an instructor and an inmate,and is also referred to as"individual interview."
How interview guidance is implemented Interview guidance is implemented routinely and also when required from an inmate or acknowledged as necessary through daily observation on inmates'clothes,facial expression,behavior,and speech patterns,etc. In interview guidance,an individual assigned teacher listens to an inmate's feelings and conflicts,and acts in various ways according to the situation. According to a survey at the time of discharge conducted by a certain juvenile training school,many inmates referred to interview guidance by individual assigned teacher as guidance that was helpful in life in the training school. Individual interview with an inmate (d) Essay guidance At juvenile training schools,inmates are made to write many essays throughout their stay.They write and elaborate essays on various subjects such as their daily life in the institution,their life related to delinquency before entering the institution,their relationships with friends,their former life at their workplace or school,etc.They are supposed to face the reality of their life and develop better ideas and sensitivity through these tasks.The central aim of essay guidance lies in taking up inmates'problems expressed in their essays and prompting them to consider these problems deeply to find out and learn a desirable life style and behavior pattern.
(e) Guidance by problem group Guidance by problem group refers to various types of guidance conducted for groups of juveniles with the same problems in common,aiming to directly prevent delinquent behavior such as drug abuse and traffic-related violations,and resolve problems related to bad friends and family conflicts that lead juveniles to delinquency.
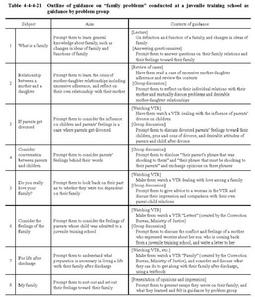
Table4-4-4-21 illustrates the outline of guidance on"family problems"conducted at a certain female juvenile training school as an example of guidance by problem group. Guidance on"family problems"aims to train inmates to objectively consider their relations with their families to learn how to restore communication with their families. Table4-4-4-21 Outline of guidance on"family problems"conducted at a juvenile training school as guidance by problem group b. Vocational guidance Juvenile training schools currently offer vocational guidance on such subjects as welding,woodwork,civil engineering and construction,operation of construction machinery,agriculture and horticulture,office work,and caretaking services,etc.Among them,guidance on caretaking services(guidance for acquiring the qualification for the second grade welfare caretaker)started in female juvenile training schools in1993,and is now conducted also in male juvenile training schools due to its significance in fostering sympathy and spiritual richness.
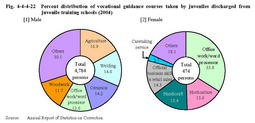
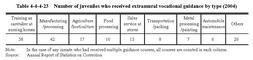
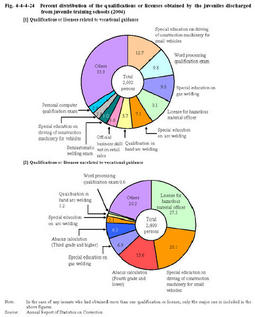
Vocational guidance(caretaking services) Vocational guidance(arc welding) In2004,93.5%of the discharged inmates took vocational guidance courses during their stay at schools. Fig.4-4-4-22 shows the percent distribution of vocational guidance courses.Fig.4-4-4-22 Percent distribution of vocational guidance courses taken by juveniles discharged from juvenile training schools(2004) Table4-4-4-23 shows the number of juveniles who received extramural vocational guidance(vocational guidance consigned to extramural facilities,etc.)in2004and the types of guidance.Table4-4-4-23 Number of juveniles who received extramural vocational guidance by type(2004) In2004,37.2%of the discharged inmates had obtained qualifications or licenses related to their vocational guidance courses,and51.5%had obtained qualifications or licenses unrelated to their vocational guidance courses.Fig.4-4-4-24 shows the percent distribution of the qualifications or licenses obtained in2004. Fig.4-4-4-24 Percent distribution of the qualifications or licenses obtained by the juveniles discharged from juvenile training schools(2004) c. Academic education Academic education is provided for(i)those who have not completed compulsory education,(ii)those who need and wish to receive senior high school education,(iii)those with poor academic ability,and(iv)those who wish to proceed to higher education or return to the schools to which they had belonged.
Academic education is conducted utilizing a Computer Aided Instruction(CAI)system,through which learners can go on studying by directly communicating with computers. Academic education(English) CAI education Of the inmates discharged in2004,115returned to junior high schools,while175returned to senior high schools.A total of350juveniles had received the graduation certificates of junior high schools while in juvenile training schools(Source:Annual Report of Statistics on Correction).Those who wish to acquire knowledge other than school education are given opportunities to take social correspondence course programs accredited by the Ministry of Education,Culture,Sports,Science and Technology.There are publicly-financed students whose school fees are borne by the government,and privately-financed students who bear their own school fees.Major courses of social correspondence course programs include bookkeeping,calligraphy/penmanship,English,electrical engineering,and lettering,etc.Including those continuing studying from the previous year,there were1,301publicly-financed students and32privately-financed students in FY2004(Source:The Correction Bureau,Ministry of Justice). d. Health and physical education Doctors and medical staff of institutions provide health and physical education on disease prevention to enhance inmates'ability to maintain good health,taking into consideration their previous delinquency and living styles.
Furthermore,in physical education,various sports activities are organized to enhance their basic physical abilities,concentration,patience,and endurance,and group games are utilized to develop compliance with rules and cooperation in interpersonal relationships. Physical education(Kendo) Physical education(running) e. Special activities Special activities are conducted mainly in groups,and include(i)voluntary activities,(ii)extramural educational activities,(iii)club activities,(iv)recreation and(v)other events.
As for voluntary activities,inmates are assigned roles such as a day manager,a book manager,a maintenance manager,a recreation manager,etc.to develop autonomy and cooperativeness at most juvenile training schools.Furthermore,meetings and homeroom activities are organized and in-house magazines are created by inmates. Volunteer work and field trips are conducted as extramural educational activities.As volunteer work,many schools implement activities at welfare facilities and cleaning/beautification activities at nearby parks and public facilities,etc.In2004,the number was highest for those who participated in"volunteer activities at nursing homes"(1,544),followed by those in"cleaning/beautification activities"(1,263)and those in"volunteer activities at facilities for the disabled"(569)(Source:The Correction Bureau,Ministry of Justice). Volunteer work (volunteer activities at welfare facilities) Volunteer work(cleaning of a park) LD/ADHD and the treatment at juvenile training schoolsRecently juveniles with non-severe developmental disorders such as learning disabilities(LD)and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder(ADHD)have become an issue.LD refers to a condition in which a juvenile has troubles in learning or using specified abilities among abilities for listening,speaking,reading,writing,calculating,or deducting.ADHD refers to a condition in which a juvenile causes various problems as he/she cannot adjust himself/herself to the surrounding environment due to a special disposition of being too restless or easily distracted,acts violently,or cannot stand frustration. Juvenile training schools provide treatment for juveniles with such mild developmental disorder,taking their disposition into consideration.At a certain male juvenile training school,treatment is implemented in the following way,designed to raise task levels gradually along with the progress of the treatment stage. (i)Level1(second grade-lower) This level aims to secure inmates'basic academic abilities such as vocabulary and calculation and basic physical strength,by repeating grammar correction of diaries,drill exercises in Japanese and arithmetic,and training for group activities,etc.For example,for enhancing inmates'functions of cooperative behavior,training for group activities focuses on training them to listen carefully to the instructors'orders and march in a certain tempo,paying attention to other inmates'movement. (ii)Level2(second grade-upper,first grade-lower) This level aims to enhance inmates'interpersonal relationships through discussion in a group of three inmates and group competition in exercises and academic studies(group jumping rope,and arithmetic drills,etc.).For example,in discussion in a group of three inmates,inmates are assigned roles as a listener,a speaker,and an observer,and are prompted to discuss repeatedly,fully aware of such key points as concentrating on the speaker's story,following up the speaker's story,and contemplating the speaker's opinions.In this way,inmates who are poor at functional listening are supposed to acquire"listening skills". (iii)Level3(first grade-upper) At this level,joint workshops for inmates and their guardians are implemented to let them discuss their worries and career courses after discharge as a practice to utilize acquired"listening skills"with their guardians. Through these levels of treatment,inmates gradually learn basic life style,academic abilities,and interpersonal abilities.Accordingly,they improve control over their impulsivity and attention-deficit hyperactivity. In this juvenile training school,various treatment methods are put into practice,responding to various inmates with mild developmental disorders,in cooperation with school officials and specialists in education for the disabled children.Overall educational effects are expected. (3) Other treatment a. Medical care and meals,etc. Of those discharged from juvenile training schools in2004,1,523(27.1%)had received some kind of medical treatment in sick rooms in schools,including those who received treatment in medical juvenile training schools.By type of illness,breathing problems had the largest share at71.0%,followed by mental or behavioral disability(7.7%),and infectious disease and parasitic disease(4.8%)(Source:Annual Report of Statistics on Correction).
Meals are provided equally except when a special meal is needed due to illness.Each meal consists of principal foodstuff and a side dish.Principal foodstuff is80%rice and20%barley.Budget for FY2005 for a side dish per inmate is502yen a day(Source:The Correction Bureau,Ministry of Justice). b. Visits and communication Visits and communication are admitted mainly for guardians,and not for friends related to delinquency.
In addition to ordinary visits admitted for a certain period of time in visiting rooms,there is a system of lodging visits,in which an inmate and his/her guardian lodge at a family dormitory(a separate building with lodging equipment)on the site of a juvenile training school to discuss family problems and life plans after discharge through a three-way interview with an instructor,etc.Lodging visits are usually admitted for inmates who are about to be discharged. Family dormitory(outside) Family dormitory(inside) (4) Cooperation and assistance from the private sector to treatment Juvenile training schools provide education in cooperation with nongovernmental volunteers in many ways.People across society,such as volunteer visitors,chaplains,members of the Women's Association for Rehabilitation Aid,and members of the BBS associations conduct supportive activities as private volunteers.
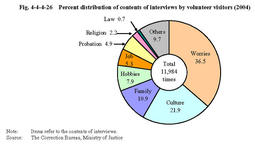
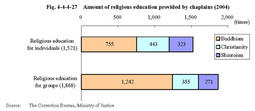
Volunteer visitors give inmates advice and guidance on mental problems and cultural guidance etc.As of December31,2004,713persons are consigned as volunteer visitors for juvenile training schools. Table4-4-4-25 shows their social status. In2004,volunteer visitors gave interview guidance11,984times. Fig.4-4-4-26 shows the percent distribution of the contents of interviews. Table4-4-4-25 Number of volunteer visitors for juvenile training schools(As of December31,2004) Fig.4-4-4-26 Percent distribution of contents of interviews by volunteer visitors(2004) Chaplains provide religious education at the request of inmates.Juvenile training schools had394chaplains(267for Buddhism,68for Shintoism,and59for Christianity)as of December31,2004. Fig.4-4-4-27 shows the amount of religious education provided by chaplains in2004.Fig.4-4-4-27 Amount of religious education provided by chaplains(2004) Members of the Women's Association for Rehabilitation Aid and members of the BBS associations regularly visit each juvenile training school to participate in school events such as birthday parties,cherry blossom viewing parties,and Coming of Age ceremonies,enjoy playing games and sports with inmates,or participate in inmates'speak-outs as judges.They offer support for educational activities in juvenile training schools in various ways.Interaction with these volunteers serves as a significant encouragement for inmates in rehabilitating themselves.Individual consultation by volunteer visitors Guidance in calligraphy by volunteer visitor Doll Festival party participated in by members of the Women's Association for Rehabilitation Aid |