| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
4 Operation of Amended Juvenile Law It has been four years since the Law for Partial Amendments to the Juvenile Law(Law No.142of2000;hereinafter referred to as the"Amended Juvenile Law"in this subsection)took effect on April1,2001.The Amended Juvenile Law consists of three major pillars;(i)review of disposition for juvenile cases,(ii)improvement in the fact-finding procedures for juvenile hearings,and(iii)enhancement of consideration towards crime victims.The law has been operating as follows.
(1) Review of disposition for juvenile cases a. Lowering of ages for prosecution The Amended Juvenile Law lowered the age possible to be prosecuted to14.Three juveniles under16were referred to public prosecutors as suitable for prosecution until2004(excluding violations of road traffic related laws),one for rape on the occasion of robbery in2002,and two for injury resulting in death in2003.The two juveniles in2003were prosecuted,but transferred to family courts by the district courts under Article55of the Juvenile Law,and were put under protective measures(commitment to juvenile training schools)(Source:The Criminal Affairs Bureau,Ministry of Justice).
b. Referral to public prosecutors for prosecution Under the Amended Juvenile Law,in cases where a juvenile aged16or over at the time of committing a crime killed a victim through an intentional criminal act(hereinafter referred to"cases where juveniles aged16or over killed victims"in this Section),he/she is supposed to be referred to public prosecutors as suitable for prosecution,in principle,unless a family court concludes that protective measures would be more appropriate.
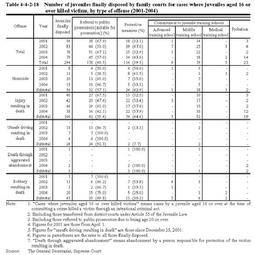
Table4-4-2-18 shows the number of juveniles finally disposed by family courts for cases where juveniles aged16or over killed victims(excluding those referred to public prosecutors due to being age20or over)since April2001,by type of offense. Table4-4-2-18 Number of juveniles finally disposed by family courts for cases where juveniles aged16or over killed victims,by type of offense(2001-2004) Among294juveniles disposed for cases where juveniles aged16or over killed victims(excluding10juveniles transferred to family courts by district courts after prosecution under Article55of the Juvenile Law),178(60.5%)were referred to public prosecutors as suitable for prosecution.The10juveniles transferred to family courts by districts courts(nine for injury resulting in death and one for robbery resulting in death)were all sent to juvenile training schools by family courts(Source:The General Secretariat,Supreme Court). The average rates of referral to public prosecutors as suitable for prosecution during ten years before the enforcement of the Amended Juvenile Law were24.8%for homicide(including attempt),9.1%for injury resulting in death,and41.5%for robbery resulting in death.After the amendment of the Juvenile Law,those rates became higher(Source:The General Secretariat,Supreme Court). c. Measures for guardians Under the Amended Juvenile Law,if family courts consider it necessary to ensure that guardians recognize their responsibility for their children,they have the authority to take appropriate measures,such as giving admonition and guidance to guardians,at the investigation or hearing by a judge or a family court probation officer.
Based on the purpose of the amendment,family courts have tried to work on guardians more actively by(i)utilizing a sheet that plainly describes the responsibilities of guardians when family court probation officers interview guardians and give them guidance,such as making them review their attitude toward child-rearing and suggesting compensation for victims,(ii)making guardians take lectures about drug abuse and traffic regulations,(iii)making juveniles and guardians jointly participate in volunteer work to improve their parent-child relation,(iv)holding guardians meetings where they can talk about their emotions and experiences to enhance their abilities,(v)making guardians listen to victims'experiences for understanding their pains,review their attitude toward child-rearing on their own,and recognize their responsibility(Source:The General Secretariat,Supreme Court). (ii) Further improvement in the fact-finding procedures a. Discretionary collegiate court system Under the Amended Juvenile Law,juvenile hearings can be conducted in the collegiate court body based on the court's discretion.
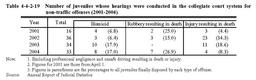
Table4-4-2-19 shows the number of juveniles whose hearings were conducted in the collegiate court system among those finally disposed for non-traffic offenses since2001,by major offense. Table4-4-2-19 Number of juveniles whose hearings were conducted in the collegiate court system for non-traffic offenses(2001-2004) b. Introduction of hearings with public prosecutors and lawyers as attendants Under the Amended Juvenile Law,a family court can have a public prosecutor attend the hearing when(i)the case is a criminal offense by a juvenile aged14-19,(ii)falling under a crime to purposely cause the death of a victim or deserving the death penalty,life imprisonment,or imprisonment(with or without labor)for not less than two years,and(iii)a family court considers it necessary for a public prosecutor to get involved in hearing procedures for fact-finding.If the juvenile does not have a lawyer as an attendant in the case which a public prosecutor is involved in,the family court must select a lawyer(public attendant).
Table4-4-2-20 shows the number of juveniles whose hearing public prosecutors attended and for whom public attendants were selected among all those finally disposed for non-traffic offenses since2001,by type of offense. Table4-4-2-20 Number of juveniles whose hearing public prosecutors attended and who had public attendants for non-traffic offenses(2001-2004) c. Extension of terms of protective detention for juveniles A family court can order protective detention for two weeks in principle,and can extend only once.Under the Amended Juvenile Law,the term can be extended two more times,for eight weeks at the longest when(i)the case is a criminal offense by a juvenile aged14-19and deserves punishment of imprisonment(any term)or death,(ii)examination of a witness,expert examination,or inspection is needed for fact finding,and(iii)there is a probable cause to extend the juvenile's detention for the court hearing.In addition,an attendant of a juvenile can make a protest against the court order of protective detention or extension of detention.
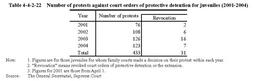
Table4-4-2-21 shows the number of juveniles whose protective detention was over four weeks. Among all those finally disposed for non-traffic offenses,99.8%juveniles in2002,99.7%in2003,and99.7%in2004were ordered protective detention of28days or less(Source:Annual Report of Judicial Statistics). Table4-4-2-21 Number of juveniles whose protective detention was extended more than four weeks(2001-2004) Table4-4-2-22 shows the number of protests against court orders of protective detention for juveniles or extension of detention since April2001.Table4-4-2-22 Number of protests against court orders of protective detention for juveniles(2001-2004) d. Appeal by public prosecutors Under the Amended Juvenile Law,a public prosecutor can appeal to a high court within two weeks from when a family court dismissed a case after hearing or ordered protective measures on the ground that there was a violation of a law or a grave error in the fact-finding that affects the court decision in a case a public prosecutor attended.
From2001to2003,public prosecutors appealed no cases.In2004,public prosecutors appealed cases of five juveniles,and the original decisions were reversed for three(Source:The Criminal Affairs Bureau,Ministry of Justice). e. Review of protective measures Under the Amended Juvenile Law,the family court that ordered a protective measure has to rescind it,as long as the juvenile is alive,after the termination of measures,if the protective measure was found to be taken without sufficient grounds for opening juvenile hearings.
During the period between April2001and the end of2004,the protective measure was rescinded for one person(professional negligence resulting in injury)(Source:The General Secretariat,Supreme Court). (3) Enhancement of consideration towards crime victims a. Inspection and copy of case files Under the Amended Juvenile Law,a victim can look through and copy the file of the case he/she was involved in at their request,if a family court permits.
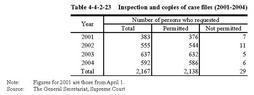
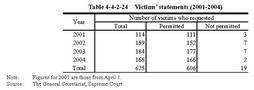
Table4-4-2-23 shows the number of victims who requested to look through or copy case files since April2001. Table4-4-2-23 Inspection and copies of case files(2001-2004) b. Victims'statements Under the Amended Juvenile Law,victims can,at their request,make their statement on their emotions and opinions over damages.
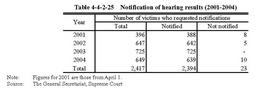
Table4-4-2-24 shows the number of victims who requested statements since April2001. Table4-4-2-24 Victims'statements(2001-2004) c. Notification of court hearing results Under the Amended Juvenile Law,a system was introduced to have family courts notify hearing results to victims at their request.
Table4-4-2-25 shows the number of victims who requested notification of hearing results since April2001. Table4-4-2-25 Notification of hearing results(2001-2004) |