| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
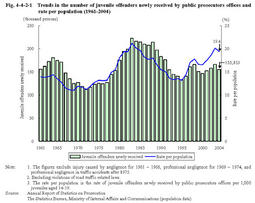
1 Disposition in public prosecutors offices (1) Cases received Fig.4-4-2-1 shows the number of juvenile offenders aged14-19newly received by public prosecutors offices(excluding those for professional negligence in traffic accidents and violations of road traffic related laws)and the rate per population(rate of juvenile offenders newly received per1,000juveniles aged14-19;hereinafter the same in this subsection)since1961.
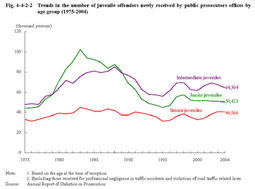
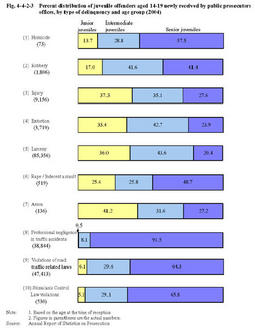
The total number of juvenile offenders newly received by public prosecutors offices in2004was241,610(the juvenile rate:11.2%).Those for penal code offenses were188,332(14.8%(id.)),among which149,488(40.7%(id.))were for non-traffic penal code offenses.Those for special law offenses were53,278(6.0%(id.)),among which5,865(5.3%(id.))were for special law offenses excluding violations of road traffic related laws(see Appendix2-1 ). Fig.4-4-2-1 Trends in the number of juvenile offenders newly received by public prosecutors offices and rate per population(1961-2004) Fig.4-4-2-2 shows the number of juvenile offenders aged14-19newly received by public prosecutors offices(excluding those for professional negligence in traffic accidents and violations of road traffic related laws)by age group.Fig.4-4-2-2 Trends in the number of juvenile offenders newly received by public prosecutors offices by age group(1975-2004) Fig.4-4-2-3 shows the percent distribution of juvenile offenders aged14-19newly received by public prosecutors offices in2004,by type of delinquency and age group(see Appendix4-8 ).Compared to the previous year,there were decreases in those newly received for homicide(down by30.5%),robbery(down by21.5%),injury(down by15.7%),extortion(down by19.4%),rape/indecent assault(down by21.8%),and larceny(down by1.8%),while there was an increase in those for arson(up by6.3%). Fig.4-4-2-3 Percent distribution of juvenile offenders aged14-19newly received by public prosecutors offices,by type of delinquency and age group(2004) (2) Referral to family courts A public prosecutor can attach his/her opinion about the treatment of the juvenile when the public prosecutor refers a juvenile case to a family court. Appendix4-9 shows the percent distribution of opinions attached by public prosecutors when referring a case to a family court(excluding those referred by summary procedure).
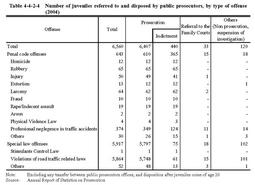
(3) Disposition of cases referred by family courts Table4-4-2-4 shows the number of juveniles disposed by public prosecutors for those referred to public prosecutors by family courts in2004.
The percentage of those who were brought to formal trial to the total prosecuted juveniles(6,407)was6.9%(up by0.6points from the previous year),and59.8%(up by3.5points(id.))for penal code offenses,and1.3%(up by0.1points(id.))for special law offenses in2004. Table4-4-2-4 Number of juveniles referred to and disposed by public prosecutors,by type of offense(2004) |