| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
4. Treatment measures for supervision (1) Classified treatment system The classified treatment system(see Part2,Chapter5,Section3-3 and Part5,Chapter5,Section4-1 )is implemented for both juvenile probationers and parolees.As of December31,2003,"Class A"juveniles who were considered to be difficult to treat accounted for5.7%of juvenile probationers and22.5%of juvenile parolees(see Fig. 2-5-3-3 ).The higher percentage of"Class A"juvenile parolees indicates that juvenile parolees were more likely to have problems that might hinder their rehabilitation.In order to carry out effective supervision of"Class A"juveniles,probation officers make more direct contact with them and closely communicate and consult with the volunteer probation officers in charge of them.
(2) Categorizedtreatmentsystem Categorized treatment(see Part2,Chapter5,Section3-3 and , Part5,Chapter5Section4-1 )is also implemented to the supervision of juvenile probationers/parolees.The categories used for juveniles include thinners and other substances abuse,stimulant drug offenses,sexual offenses,junior high school students,unemployed juveniles,and bosozoku etc. Table 4-2-6-7 shows the percentage of juvenile probationers and parolees identified in major categories under supervision as of December31,2003.Among both probationers and parolees,the percentage of bosozoku was highest,followed by thinners abuse.Among juvenile parolees,in particular,bosozoku reached27.7%and thinner abusers reached15.2%.Probation offices set supervision guidelines for each category,and probation officers and voluntary probation officers conduct supervision following them.Some offices organize group treatment programs for thinners and stimulant drugs abusers.Group treatment programs sometimes are provided not only to the juveniles in question but also to their families.
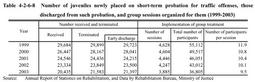
As described in Part5,Chapter5,Section4-1 ,the revised categorized treatment system has been in place since April2003.Since the revision,the category of"family violence"has been expanded to cover violence to children such as sexual abuse,neglect,and psychological abuse. Table 4-2-6-7Percentage of juvenile probationers/parolees newly placed under supervision by treatment category(as of December31,2003) (3) Short-termprobationfortrafficoffenses Short-term probation for traffic offenses is conducted under a probation order decided by a family court.A juvenile who is placed on it attends a group treatment program on safe car driving instead of individual supervision by probation officers and volunteer probation officers.He or she is also required to submit a monthly report on his or her life in writing.If the juvenile does not repeat a traffic offense,he or she is discharged from probation after a short period of three or four months in principle. Table 4-2-6-8 shows the number of juveniles who were newly placed under short-term probation for traffic offenses,of those who were discharged from such probation,and of group sessions organized for them in the last five years.
Table 4-2-6-8Number of juveniles newly placed on short-term probation for traffic offenses,those discharged from such probation,and group sessions organized for them(1999-2003) (4) Short-term probation for non-traffic offenses Short-term probation for non-traffic offenses is for a juvenile who is placed on probation by a family court order for any offense other than professional negligence in a traffic accident or violations of road traffic-related laws as long as the juvenile has not developed strong delinquent tendencies and is expected to improve and rehabilitate him/herself during the short-term period.It is conducted through individual supervision by a probation officer and volunteer probation officer for the short period of six or seven months in principle.In the supervision of a juvenile,targeting areas are specified such as his/her lifestyle,school life,employment,family relationships,or friends etc.that he/she has problems with and is particularly important for his/her rehabilitation,and some assignments are given for him/her to perform designed to help him/her solve their problems.
(5) Participation programs in social activities In addition to individual supervision by a probation officer and volunteer probation officer,a probationer/parolee is encouraged to participate special programs in social activities.It aims to help a probationer/parolee develop his/her skills by participating in various activities including community services such as cleaning parks and assisting in nursing care in homes for the aged as well as sports,creative activities,and experiential learning activities.The programs are implemented mainly for juvenile probationers and often recommended as an assignment for a juvenile under short-term probation for non-traffic offenses.In FY2003,they were organized593times nationwide(513in the previous year),with the participation of1,599probationers/parolees(1,587in the previous year)(Source:Data by Rehabilitation Bureau,Ministry of Justice).
|