| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
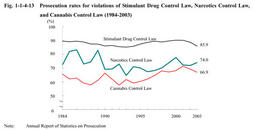
3. Treatment of drug offenders (1) Disposition by public prosecutors Fig. 1-1-4-13 shows prosecution rates for violations of Stimulant Drug Control Law,Narcotics Control Law,and Cannabis Control Law over the last20years.Prosecution rate for Stimulant Drug Control Law violations was within the85-90%range,except for over90%in2000and2001.The rate for Narcotics Control Law violations fell to64.7%in1993,but then generally rose to74.0%in2003.The rate for Cannabis Control Law violations generally rose since1995,to the highest level over the last20years in2001at71.4%,but then declined to66.9%in2003(see Appendix1-6 ).
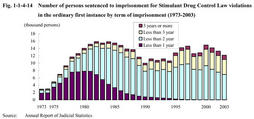
Fig. 1-1-4-13 Prosecution rates for violations of Stimulant Drug Control Law,Narcotics Control Law,and Cannabis Control Law(1984-2003) (2) Disposition in courts Fig. 1-1-4-14 shows the number of persons sentenced to imprisonment with labor for Stimulant Drug Control Law violations in the ordinary first instance since1973,by the term of imprisonment.
The percentage of less than one year imprisonment dropped sharply after a peak of7,793(55.5%)in1980,to36(0.3%)in2003.In contrast,the percentage of imprisonment for two years or more but less than three years has increased from208(7.1%)in1973to4,057(33.3%)in2003,which indicates that sentences for drug cases have become gradually heavier(For details,see Part5,Chapter3,Sections1-4 ). Fig. 1-1-4-14 Number of persons sentenced to imprisonment for Stimulant Drug Control Law violations in the ordinary first instance by term of imprisonment(1973-2003) (3) Correction Stimulant Drug Control Law violations are one of the most common types of offense among inmates detained in correctional institutions.Correctional institutions have special treatment programs for the education of those inmates imprisoned for Stimulant Drug Control Law violations.Recent such education programs are marked by employing various staff members,not only staff in institutions but also outside professionals.
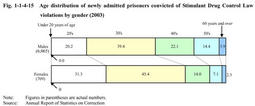
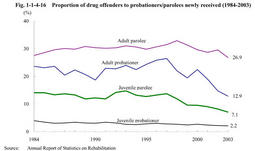
Fig. 1-1-4-15 shows age distribution of newly admitted prisoners convicted of Stimulant Drug Control Law violations in2003.Those aged30-39were the largest group for both females and males,while those aged50-59or60or over have increased gradually(For details,see Part5,Chapter3,Section2-4 ). Fig. 1-1-4-15 Age distribution of newly admitted prisoners convicted of Stimulant Drug Control Law violations by gender(2003) (4) Rehabilitation Fig. 1-1-4-16 shows proportion of drug offenders(those who commit violations of the Narcotics Control Law,Stimulant Drug Control Law,or Poisonous and Deleterious Substances Control Law)to probationers/parolees newly received over the last20years.The proportion of drug offenders in adult parolees declined after a peak in1998.The proportion in adult probationers also declined after a peak in1997.
Probation offices endeavor to improve probation programs for drug offenders,by classifying them intostimulant drug offenders"andabusers of thinners,etc."in the categorized treatment system.The offices also try various treatment practices,such as providing group guidance to probationers/parolees and their guardians and guarantors(For details,see Part5,Chapter5,Section2-3 ). Fig. 1-1-4-16 Proportion of drug offenders to probationers/parolees newly received(1984-2003) Explanation of termsMoney laundering: Money laundering refers to the process by which offenders conceal or disguise the origin of proceeds of drug offenses,etc,and make the proceeds look like profits gained from legal commercial transactions,such as,the act of transferring money through a series of bank accounts. Controlled delivery: Controlled delivery refers to an investigative technique in which the police,etc.allow specific consignments of illicit drugs to be distributed under close observation without immediate seizure in order to trace the distribution channel and identify the persons involved in the transactions. On the other hand,"clean controlled delivery"refers to an investigative technique that removes illicit drugs which were discovered by the police,etc.,but allows a consignment of alternatives substituted for the illicit drugs to be distributed. |