| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
4. Treatment of inmates in juvenile trainingschools In line with the purpose of the Juvenile Law that ensures the sound development of juveniles,juvenile training schools provide delinquents with systematic treatment to achieve the goals of correctional education,such as correcting their problems leading to delinquency,eliminating causes for their maladjustment to society,and giving them the ability to adjust to social life.
(1) Individualized treatment and classification system The individualization of treatment,one of the basic principles in correctional education at juvenile training schools,means to provide treatment tailored according to the needs of each juvenile with due consideration for his or her personality,good points,preferences for future career options,mental and physical conditions,and delinquent tendency etc.
For individualized treatment,the classification treatment system is established,under which scientific researches are conducted on juvenile inmates individually,to classify them into different groups according to their characteristics and educational needs,and to provide each group with the most appropriate treatment program. (2) Progressive grade system Different grades of treatment are given to inmates in juvenile training schools.Inmates are classified into the first grade,second grade or third grade under the relevant regulations.The first grade and the second grade are divided into the upper one and the lower one.Those newly admitted to training schools are placed in the lower second grade and then move up to higher grades according to their improvement.If they had bad records,they might be demoted in the third grade.
The progressive grade system is not implemented for inmates uniformly for the entire term of their detention but on a case-by-case basis based on the treatment goals,contents,and methods chosen for each grade of improvement.The treatment is designed to encourage inmates to improve themselves and to make efforts voluntarily and thereby to facilitate their improvement so that they can attain their goals as soon as possible. Since treatment of inmates needs to be systematic from their admission to release,the treatment process is divided into three stages:the orientation stage,intermediate stage,and pre-release stage.As an inmate moves from one stage to the next,he/she will be faced with higher educational goals and more advanced educational contents than at the previous stage. In principle,the educational stages and progressive grades correspond to each other as follows.The orientation stage corresponds to the lower second grade,intermediate stage to the upper second grade and the lower first grade,and pre-release stage to the upper first grade. (3) Educational activities Educational activities are divided into the following five areas:living guidance,vocational guidance,academic education,health and physical education,and special activities.These areas supplement one another.
a. Living guidance Living guidance plays a central role in correctional education of juvenile training schools to give inmates the ability to lead a sound social life.The guidance is formulated in consideration of a juvenile's character,living experience,way of thinking and interpreting things,values,and problems leading to delinquency.It is given at every opportunity available in juveniles'daily life in training schools.While maintaining a balance between individual guidance and group guidance,juveniles are trained to establish better interpersonal relationships and increasing self-awareness through mutual interaction in their group living.It is given in an organized and systematic way by closely connecting with other areas of guidance.In addition,under the amended Juvenile Law enforced in2001,juvenile training schools have enhanced to incorporate the crime victims views into their education programs and have strengthened their efforts to communicate with the parents of inmates.
The contents of the living guidance are as follows: (i)Guidance for solving problems related to his or her ways of thinking,attitude,and behavior that could lead to delinquency; (ii)Therapeutic treatment to solve problems related to his or her predisposition; (iii)Sentiment education; (iv)Guidance to improve his or her basic living skills and interpersonal relationships and to promote law-abiding and self-disciplinary behavior; (v)Guidance to solve problems in relationships with his or her family and friends after his or her release; (vi)Guidance to prepare him or her for career selection,life planning,and social rehabilitation. b. Vocational guidance Vocational guidance is designed to help juveniles develop their will to work as well as the ability to select their vocations according to their individual characters.The guidance for junior juveniles is to give them basic vocational knowledge and skills and to cultivate their ability to apply them.For intermediate and senior juveniles,it is to give them the knowledge and skills necessary to support themselves and an ability to apply them.
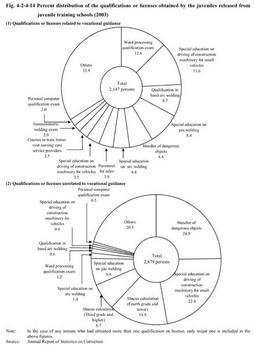
Vocational guidance includes various areas as follows: (i)Production training to improve vocational awareness,knowledge,and skills etc.,skill training according to the skills of inmates,vocational information services,consultation and advice on vocational life; (ii)Vocational training based on the Human Resource Development Promotion Law and other related laws and regulations;and (iii)Extramural vocational guidance given by external business entities for advanced-level training of(i)and(ii)or for a smooth transition of inmates to social life. Juvenile training schools currently offer vocational guidance on such subjects as welding,woodwork,civil engineering and construction,operation of construction machinery,agriculture and horticulture,and office work etc.The goal of any vocational guidance course is for an inmate to obtain official qualifications or licenses related to the course.Inmates are also encouraged to obtain other qualifications or licenses which are not related to their vocational courses but useful in their working lives after their release. Fig. 4-2-4-14 shows the percent distribution of the qualifications or licenses obtained through vocational guidance by the juveniles released in2003.In2003,a37.1%of the released inmates had obtained qualifications or licenses related to their vocational guidance courses,an increase of1.8points compared to the previous year.A49.7%had obtained qualifications or licenses unrelated to their vocational guidance courses,an increase of3.6points from the previous year. Also,a total of325or5.6%of the inmates released in2003had received extramural vocational guidance(Source:Annual Report of Statistics on Correction). Fig. 4-2-4-14Percent distribution of the qualifications or licenses obtained by the juveniles released from juvenile training schools(2003) c. Academic education Those inmates who have not completed compulsory education are placed in the academic education course,in which curriculum for junior high school education is systematically organized based on the Education Ministry's guidelines,and guidance for inmates to prepare the entrance examination of senior high schools and other guidance are given according to their preference after completing compulsory education.Those who desire to receive senior high school education are admitted to high schools with correspondence course programs.Those who desire to enter universities are given opportunities to take the University Entrance Qualification Examination organized by the Education Ministry and given supplementary assistance in their preparing for the examination.Also,necessary guidance is given for those inmates with poor academic ability and for those who wish to return to the schools they had belonged.Furthermore,those who wish to acquire knowledge other than school education are given opportunities to take social correspondence course programs accredited by the Education Ministry,such as bookkeeping,electrical engineering,calligraphy/penmanship,and lettering etc.
Of the inmates released in2003,108returned to junior high schools,while139to senior high schools.A total of332juveniles had received the graduation certificates of junior high schools while in juvenile training schools(Source:Annual Report of Statistics on Correction). d. Healthandphysicaleducation Health and physical education in juvenile training schools aim at the restoration and improvement of inmates'physical health and cultivation of their concentration,endurance,and stamina.Such education is important since most inmates had unhealthy lifestyles before their entering training schools.Taking into consideration their previous delinquency and living styles,health education provides guidance on their health care and disease prevention,whereas various sports activities are organized to enhance their basic physical abilities,compliance with rules and cooperation in interpersonal relationships.
e. Specialactivities Special activities are conducted mainly in groups,and include(i)voluntary activities,(ii)extramural educational activities(field trips,volunteer work etc.),(iii)club activities,(iv)recreation and(v)other events.Special activities assume the critical role of making use of inmates'leisure hours and enriching their juvenile training school life.
(4) Medicalcareandsupplies It is important to maintain and improve inmates'health to achieve their correctional education goal.Each juvenile training school has a Medical Division and full-time doctors.Normal diagnosis is performed at each institution.However,those who require special or long-term medical care are admitted to medical juvenile training schools.Juveniles may receive treatment at proper outside hospitals as inpatients or outpatients if necessary.
Of those released from juvenile training schools in2003,1,761(30.4%)had received some kind of medical treatment in sick rooms in schools,including those who received long-term treatment in medical juvenile training schools.By type of illness,breathing problems had the largest share at71.8%,followed by mental or behavioral disability(7.8%),and digestive problems(4.5%)(Source:Annual Report of Statistics on Correction). For basic living supplies-food,clothing,and shelter-juvenile training schools lend or provide clothes,bedding,stationary goods,and other supplies necessary for daily life.Food is provided based on the authorized standard quantities of nutrients necessary per day. (5) Cooperation and assistance from the private sector Juvenile training schools provide education in cooperation with nongovernmental volunteers in many ways.One of them is consultation activities conducted by volunteer visitors and chaplains for inmates.Volunteer visitors give inmates advice on mental problems and cultural guidance etc.,while chaplains perform individual consultation at the request of inmates.Juvenile training schools had722volunteer visitors and367chaplains as of December31,2003(Source:Data by Correction Bureau,Ministry of Justice).
In addition,some education programs are carried out outside juvenile training schools by social resources which are entrusted the implementation of education programs by training schools.Under those programs,inmates go out and receive vocational guidance in private companies or attend outside schools for academic education. |