| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
3 Characteristics of newly imprisoned offenders (1)Age
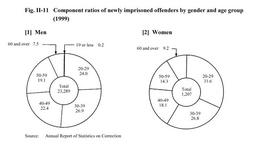
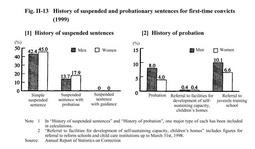
Fig. II-11 shows the component ratios of newly imprisoned offenders in 1999 by gender and age group. Fig. II-11 Component ratios of newly imprisoned offenders by gender and age group (1999) Of newly imprisoned offenders in 1999, 1,850 were aged 60 or over, representing 7.6% of the total. Japan has no specially designated facilities to accommodate older inmates aged 60 or over. Instead, they are housed in various correctional institutions in accordance with the category of their detention.(2)Offenses Of the offenses committed by newly imprisoned offenders in 1999, viewing the 5 most common offenses for each gender, the sequence among male inmates was [1] larceny (29.7%), [2] Stimulant Drug Control Law violations (23.3%), [3] fraud (6.6%), [4] Road Traffic Law violations (6.5%), and [5] bodily injury (5.4%). For female inmates, the 5 most common offenses were [1] Stimulant Drug Control Law violations (47.4%), [2] larceny (20.5%), [3] fraud (8.5%), [4] homicide (4.6%), and [5] Road Traffic Law violations (2.6%) (see Appendix II-7 ). (3)Type of sentence and imprisonment term Of the types of sentence of newly imprisoned offenders in 1999, 99.2% (24,293 inmates) were sentenced to imprisonment with labor, followed by imprisonment without labor with 0.6% (159), penal detention with 0.2% (39), and the death penalty (executed) with 0.02% (5). Fig. II-12 shows the component ratios of newly imprisoned offenders sentenced to imprisonment with labor in 1999, by length of sentence. Fig. II-12 Ratios of newly imprisoned offenders sentenced to imprisonment with labor, by length of sentence (1999) (4)History of suspended and probationary sentences for first-time convicts Fig. II-13 shows a breakdown of the 11,113 first-time convicts(that is, persons entering correctional institutions for the first time after sentencing by a court)newly imprisoned in 1999, according to their respective histories of suspended and probationary sentences. Fig. II-13 History of suspended and probationary sentences for first-time convicts (1999) (5)Frequency of imprisonment Of offenders newly imprisoned in 1999, the ratio of repeat imprisonment(inmates who had previously been admitted to a correctional institution at least once) was 55.7% for men and 33.5% for women. By offense, the highest for men was larceny (34.6%) and for women, Stimulant Drug Control Law violations (54.0%). Meanwhile, 5,586 newly imprisoned offenders (22.8% of the total) had previously been imprisoned at least 4 times. Of these, by offense, violations of the Law Concerning Punishment of Physical Violence and Others accounted for 39.3% and breaking & entering for 39.1% (see Appendix II-8 and II-9 ). |