| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
3 Analysis by classification type of offenses We have so far made an analysis mainly by type of offenses but for deepening the understanding of serious juvenile offense cases,we analyzed by classification type of offenses to examine the individual characteristics.
In the analysis,serious juvenile offense cases were divided into general offenses and traffic offenses,and traffic offenses were named as"Traffic Type,"while those general offenses where juveniles and victims are related(including cases where a juvenile killed his/her lover's child)as"Family Type."Other general offenses were classified into"Group Type"and"Single Type"according to the presence or absence of accomplices. (1) Characteristics by classification type of offenses a. Group Type(offenders committing a crime with a ccomplices) Group Type cases are most common in serious juvenile offense cases.
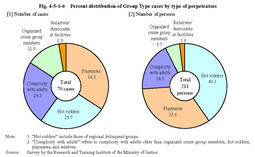
An example of Group Type cases(male) -A case in which a group of juveniles called a victim late at night just because he had spoken ill of the hot rodders group,lynching him in a group,causing death Although the victim strongly denied having spoken ill of the group,the group of juveniles became convinced of his telling a lie and started lynching him.They continued beating and kicking the passive victim for hours. Injury resulting in death is the most common type of serious juvenile offenses in the Group Type cases,and the percentage is high for juvenile offenders with a history of protective measures and those belonging to delinquent groups.Those who go to schools are short on motivation to learn,and many juveniles classified into this type associate with bad companies in the region with little motivation to work,or belong to delinquent groups that end up committing serious offenses swayed by mass psyche. Fig.4-5-1-6 shows the percent distribution of Group Type cases by type of perpetrators."Complicity with adults"refers to complicity with adults other than organized crime group members,hot rodders,playmates,and relatives.Most Group Type cases were committed by males,but there were nine females among211,of whom seven committed offenses with adults,one with relatives and one with playmates.In many cases,females followed their senior lover to commit an offense. Fig.4-5-1-6 Percent distribution of Group Type cases by type of perpetrators Breaking down Group Type cases by type of perpetrators,lynching in groups was most common in cases by hot rodders,among which major ones were cases of group lynching against a member who declared defection from the group.There were also cases of group lynching by playmates against a peer in a vulnerable position due to trifles such as the peer having told a lie or spoken ill of somebody.In contrast,in cases by organized crime groups,there were cases in which trivial troubles,which group members had at restaurants or on roads caused by their habitual violent behavior and excitement with drinks,escalated into a fight to kill victims.In some cases,non-severe violence that started to slightly hurt the victims escalated into severe violence,swayed by mass psyche.In particular,group lynching cases without a clear leader are apt to escalate into serious ones. b. Single Type(offenders committing a crime without a ccomplices) Compared to other classification types,juveniles classified into the Single Type were smallest in number at16.Most of them were males and there was only one female.
An example of Single Type cases(male) -A case of homicide on the occasion of robbery committed by a male who was pessimistic about his future The juvenile,who had failed in finding a job and was scolded by his parents,ran away from home,and decided to kill the victim,who had kindly offered him a sleeping place,to obtain his money.The juvenile swung down the iron pipe from behind the victim,beat him on the head repeatedly to death,and robbed his money. Among Single Type cases,cases of fights were largest in number,involving eight juveniles(50.0%),followed by troubles with the opposite sex involving four(25.0%),and others involving four(25.0%).Each type of case was committed by juveniles with distinctive characteristics. Eight juveniles involved in fights can be classified into the Isolated Event Type and the Violent Type.Four juveniles classified in the Isolated Event Type had no history of offenses and showed no notable tendencies of disorderly life or violence.In contrast,the four other juveniles of the Violent Type had been brought up under an unstable environment,such as in a broken family or in a disfunctional family,or among an abusive relationship with their mother.They have hyperactive natures and have shown a notable violent tendency with a history of repeated fights since their elementary school days. Four juveniles involved in troubles with the opposite sex ended up killing their lover with emotional entanglements.These juveniles did not have a serious history of offenses,but could not resolve their entangled relationships,which led them to kill their lover impulsively.In one case,a juvenile,who had chosen a life of refraining from expressing his real or honest feelings,could not deal with the emotional entanglements with his lover appropriately,resulting in killing her by acts driven by wild emotion. The four other juveniles committed heinous crimes,such as homicide on the occasion of robbery or arson resulting in death,but the gap between motives and the heinousness of the results was too large,or the motives themselves were incomprehensible and mental disabilities were suspected.In a case of homicide on the occasion of robbery,the juvenile,who had once got employed and started a life as a member of society,could not feel confident about his future and lost his reason for living,resulting in committing a serious crime while he had completely lost his usual normative consciousness and consideration towards others.In a case of arson resulting in death,the juvenile blamed people around him for all his misfortunes and committed a serious crime,trapped in a morbid delusion.In these cases,juveniles had developed emotional failure and frustrations inside of themselves,and such emotions drove them to take on aggressive behaviors. c. Family Type Family Type cases are the second largest in number among serious juvenile offense cases.
An example of Family Type cases(male) -A case in which a juvenile unleashed violence on his drunken father,causing injury resulting in death Since his mother left home due to his father's excessive drinking and domestic violence,the juvenile had replaced his mother and had taken care of his younger brothers.He had built animosity toward his father who did not work and did nothing but drink every day.At the time of this case,he saw his father asleep in a state of complete drunkenness without going to work,and resorted to violence,exploding out of a grudge toward him,who had caused the present difficult circumstances. Juveniles classified into the Family Type are younger at the time of offense,and the percentage of students and pupils is higher,compared to that of other classification types.More than half of the females who committed serious juvenile offense cases are classified into this type.Most juveniles of this type have no history of receiving disposition of protective measures,but have suffered from various problems in their families,such as conflicts among family members.On the surface,they have no history of offenses and have no bad company,but cannot release their stress without any suitable persons to consult with on their worries about family.Males are apt to resort to violence,triggered by trifles,and females often end up abusing their own child. Among victims of Family Type cases,children are largest in number at12(42.9%),followed by fathers at eight(28.6%),mothers and brothers both at three(10.7%),and a grandfather and a grandmother both at one(3.6%).There were12females classified into the Family Type,among whom10were involved in cases where their children were victims. Fig.4-5-1-7 shows the percent distribution of Group Type cases by type of victims and offenses. Homicide had the largest percentage,but87.5%of cases where fathers were victims were injury resulting in death. Fig.4-5-1-7 Percent distribution of Group Type cases by type of victims and offenses Among cases where children are victims,nine were infanticide by females,two were torture resulting in death,and one was neglect.By type of offense,most of the homicide cases were infanticide,cases of torture resulting in death were injury resulting in death,and a case of neglect was abandonment by a person responsible for protection of the victim resulting in death.Females who killed their new-born babies were all unmarried and did not tell their family about their pregnancy.Cases where fathers were victims were all committed by male juveniles.Most of those male juveniles s had a history of family violence,and some of their fathers seemed to have had problems such as excessive drinking or violence. In contrast,in cases where mothers were victims,most mothers did not have any notable problems.There were cases where a juvenile seemed to have had some mental disabilities,and where a juvenile who had wished to kill himself ended up killing his mother. d. Traffic Type Traffic Type cases were all unsafe driving resulting in death committed by males.
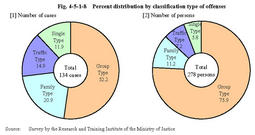
An example of Traffic Type cases -A case of unsafe driving resulting in death which caused the death of fellow passengers This is a case in which a juvenile drove a car without a license,failed to negotiate a curve due to speeding and darted off of the road,resulting in killing his fellow passengers. After enjoying drinking,the juvenile went for a drive with his fellow workers at their invitation.They got excited while they were talking.The juvenile sped up,approached the curve at top speed,and caused the accident. Juveniles classified into the Traffic Type are relatively old at the time of offense,compared to other classification types.The percentage of those employed is rather high,and they seldom have a history of belonging to any Hot rodders groups.Furthermore,the percentage of those who have a history of unlicensed driving is around half of that of the Group Type juvenile offenders.A high percentage of them have birth parents as their guardians,and seldom have any family problems.Many of them had been raised in a friendly family environment without committing any notable delinquency,had gotten employed and led a life as a normal member of society.But they caused serious results by driving a car due to their disregard of traffic rules. Traffic Type cases were most frequently caused by speeding(13juveniles or65.0%),followed by disregarding a traffic light(five juveniles or25.0%),and drunken driving(two juveniles or10.0%).There were nine single vehicle crashes,five accidents with other vehicles,four accidents with pedestrians,one accident with a motor bike,and one accident with a bicycle.Two juveniles out of the20drove a car without a license,and three ran away after the accident. (2) Analysis by comparison among classification types of offenses Fig.4-5-1-8 shows the percent distribution by classification type of offenses.
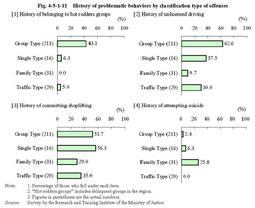
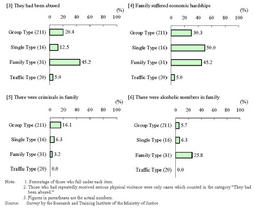
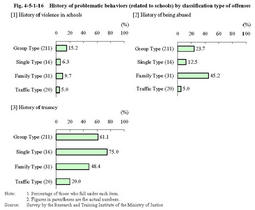
When we refer to the average age at the time of offenses,Family Type juvenile offenders were youngest at16.8years of age,followed by Group Type juvenile offenders at17.0,Single Type juvenile offenders at17.1,and Traffic Type juvenile offenders at18.4.By sex,Traffic Type juvenile offenders were all males,and95.7%of Group Type juvenile offenders and93.8%of Single Type juvenile offenders were males.In contrast,the Family Type included a higher percentage of females(38.7%),but this was because this type included females who committed infanticide. Fig.4-5-1-8 Percent distribution by classification type of offenses Fig.4-5-1-9 shows the percent distribution by classification type and type of offenses.Fig.4-5-1-9 Percent distribution by classification type and type of offenses Fig.4-5-1-10 shows a history of receiving disposition of protective measures by classification type of offenses.Compared to overall juveniles newly admitted to juvenile classification homes in2003,serious juvenile offenders showed a lower percentage for those who had a history of being committed to juvenile training schools and placed under probationary supervision.In particular,there were no Family Type juvenile offenders who had a history of being committed to juvenile training schools and placed under probationary supervision,and no Traffic Type juvenile offenders who have a history of being committed to juvenile training schools. Fig.4-5-1-10 History of receiving disposition of protective measures by classification type of offenses Fig.4-5-1-11 shows a history of problematic behaviors by classification type of offenses.Compared to other classification types,the Group Type showed a relatively higher percentage for those who had a history of belonging to hot rodders groups and a history of unlicensed driving.In contrast,the Family Type showed a slightly higher percentage(25.8%)for those who had attempted suicide. Fig.4-5-1-11 History of problematic behaviors by classification type of offenses Fig.4-5-1-12 shows the percent distribution by guardian and classification type of offenses.80%of Traffic Type juvenile offenders had birth parents as their guardians,showing a much higher percentage than that among overall juveniles newly admitted to juvenile classification homes in2003(52.9%).In contrast,the percentage of Family Type juvenile offenders who had birth parents as their guardians was48.4%,slightly lower compared to other types. Fig.4-5-1-12 Percent distribution by guardians and classification type of offenses Fig.4-5-1-13 shows family problems by classification type of offenses.More than half(61.3%)of Family Type juvenile offenders suffered from family conflicts,and the percentage was higher for those who had alcoholic family members or had been abused,compared with other types.In contrast,Traffic Type juvenile offenders had no notable family problems. Fig.4-5-1-13 Family problems by classification type of offenses Fig.4-5-1-14 shows a history of domestic problematic behaviors by classification type of offenses.The percentage of running away from home was higher for Group Type juvenile offenders and Single Type juvenile offenders,showing strong tendencies to try to escape from custody areas by guardians,etc.In contrast,a higher percentage was observed for Family Type juvenile offenders with a history of family violence,but the percentage of those with a history of running away from home was rather low.Taking the above-mentioned survey results on family problems(see Fig.4-5-1-13 )into consideration,it seems that Family Type juvenile offenders have various family problems but are unable to escape from them,hoarding frustration inside of themselves. Fig.4-5-1-14 History of domestic problematic behaviors by classification type of offenses Fig.4-5-1-15 shows the percent distribution by educational and employment situation and classification type of offenses.65.0%of Traffic Type juvenile offenders are employed,while50.0%of Single Type juvenile offenders are unemployed.There were few employed juvenile offenders in the Family Type,and the percentage of students and pupils was high at61.3%.The Group Type showed almost the same percent distribution as those newly admitted to juvenile classification homes in2003. Fig.4-5-1-15 Percent distribution by educational and employment situation and classification type of offenses Fig.4-5-1-16 shows a history of problematic behaviors(related to schools)by classification type of offenses.Fig.4-5-1-16 History of problematic behaviors(related to schools)by classification type of offenses Fig.4-5-1-17 shows the percent distribution of histories of receiving disposition,etc.by classification type of offenses.The figures show the percent distribution of the following by classification type of offenses;(i)those who have received disposition of any kind of protective measures by family courts,(ii)those who have not received disposition of protective measures but have received disposition of dismissal without hearing or dismissal after hearing by family courts,(iii)those who have not received disposition of protective measures nor disposition of dismissal without hearing or dismissal after hearing by family courts,but have had problematic behaviors,such as belonging to hot rodders groups,unlicensed driving,violence upon themselves,running away from home,truancy,family violence,violence in schools,attempted suicide,or shoplifting,and(iv)those without any of these histories.As referred to in Fig.4-5-1-10 ,serious juvenile offenders showed a lower percentage for those with a history of receiving disposition of protective measures,compared with overall juveniles newly admitted to juvenile classification homes.They seem to have committed serious offenses"abruptly,"but actually they have not been free from problems.Many of them had received disposition of dismissal without hearing or dismissal after hearing,or had had some problematic behaviors such as belonging to hot rodders groups,prior to their serious offenses.In particular,there were only less than10%of Group Type juvenile offenders who had no histories of offenses or problematic behaviors.Many juveniles of this type seem to have learned a culture of delinquency through relationships with bad company.The Family Type showed a low percentage(3.2%)for those with a history of receiving disposition of protective measures,but the percentage was high for those with family conflicts and domestic problematic behaviors including family violence.Only Traffic Type juvenile offenders showed a high percentage(45.0%)for those without any histories of offenses or problematic behaviors.A relatively high percentage of them seem to have not shown any significant sign of a disorderly life prior to their serious offenses. Fig.4-5-1-17 Percent distribution of histories of receiving disposition by classification type of offenses |