| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
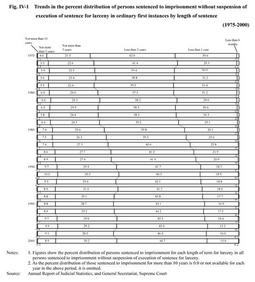
(See Fig. IV-1 )
The number of suspects prosecuted for larceny by public prosecutors offices, which decreased during the period from 1975 to 1991, has been consistently increasing since 1997. Viewing the persons sentenced to imprisonment without suspension of execution of sentence for larceny in ordinary first instances by length of sentence, the percent distribution of persons sentenced to imprisonment for"less than 1 year"and"less than 6 months"dropped almost by half from 31.6% in 1975 to 15.8% in 2000. On the contrary, the percent distribution of those sentenced to imprisonment for other lengths of terms from"less than 2 years"to"not more than 10 years"increased. More specifically, in 2000, nearly 50% of the persons sentenced to imprisonment without suspension of execution of sentence were sentenced to imprisonment for"less than 2 years". Among the persons granted a suspended sentence, those sentenced to imprisonment for"not more than 3 years"and for"less than 2 years"significantly increased their shared percent distributions. Terms of imprisonment for other general penal code offenses are also addressed here. With respect to the four types of offenses that have been significantly rising in number, i. e. robbery, bodily injury, indecent assault, and destruction of objects, the term of sentence has been getting longer since 1975. The percentage of persons sentenced to imprisonment without suspension of execution of sentence has been increasing in the case of robbery, while it has decreased or remained stable in the case of the other three types of offense. Fig. IV-1 Trends in the percent distribution of persons sentenced to imprisonment without suspension of execution of sentence for larceny in ordinary first instances by length of sentence (1975-2000) |