| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
1 Admission and discharge
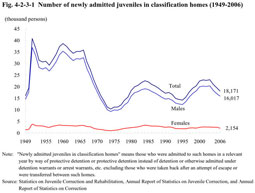
(1) Number of newly admitted juveniles in classification homes
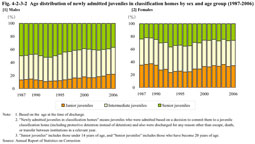
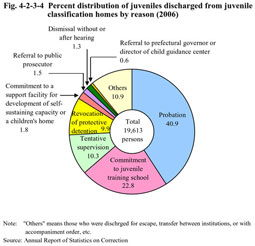
Fig. 4-2-3-1 shows the change in the number of juveniles newly admitted to juvenile classification homes since 1949. Fig. 4-2-3-1 Number of newly admitted juveniles in classification homes (1949-2006) The number of newly admitted juveniles increased from 1996, marking a record high since 1970 in 2003, but decreased compared to the previous year in 2004, 2005, and 2006 consecutively (see Appendix 4-11). Among newly admitted juveniles in 2006, those admitted by way of protective detention accounted for 84.7% and those by protective detention instead of detention accounted for 11.3% of the total. There were also very few juveniles admitted by way of detention or custody, etc. (Source: Annual Report of Statistics on Correction).(2) Characteristics of newly admitted juveniles Fig. 4-2-3-2 shows the age distribution of newly admitted juveniles in classification homes over the last 20 years by sex. Fig. 4-2-3-2 Age distribution of newly admitted juveniles in classification homes by sex and age group (1987-2006) For both males and females, the ratio of senior juveniles is on a downward trend, while that of younger juveniles is on an upward trend, and comparison between males and females shows that the ratio of younger juveniles admitted to classification homes is higher in females.Fig. 4-2-3-3 shows the percent ratio of newly admitted juveniles in classification homes in 2006 by sex, age group and type of delinquency. Fig. 4-2-3-3 Percent distribution of newly admitted juveniles in classification homes by sex, age group, and by type of delinquency (2006) For males, theft accounted for the highest proportion among all age groups. In females, as the age group shifts from junior to senior, the ratio of pre-delinquency decreases, while that of Stimulants Control Act violations increases.(3) Reasons for discharge Fig. 4-2-3-4 shows the percent distribution of juveniles discharged from juvenile classification homes by reason. Fig. 4-2-3-4 Percent distribution of juveniles discharged from juvenile classification homes by reason (2006) The ratio for probation was the highest, followed by commitment to juvenile training schools. |