| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
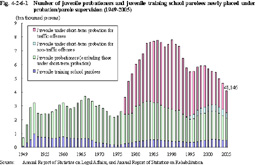
1 Juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees (1) Total number Fig. 4-2-6-1 shows the number of juvenile probationers and juvenile training school parolees newly placed under probationary supervision since 1949.
Fig. 4-2-6-1 Number of juvenile probationers and juvenile training school parolees newly placed under probation/parole supervision (1949-2005) There are short-term probation for non-traffic offenses and short-term probation for traffic offenses determined by recommendation concerning treatment by a family court.a. Short-term probation for non-traffic offenses Short-term probation for non-traffic offenses is for a juvenile who is placed under probation by a family court order for any offense other than traffic-related ones (dangerous driving causing death or injury, negligence in the pursuit of social activities in traffic accidents, violations of four statute traffic related acts, and Road Trucking Act violations; hereinafter the same in this Section) as long as the juvenile has not developed strong delinquent tendencies and is expected to improve and rehabilitate him/herself during the short-term period. This has been conducted since 1994, and 4,271 juveniles were newly placed under short-term probation for non-traffic offenses in 2005.
Short-term probation for non-traffic offenses lasts for a short period of six or seven months in principle, during which treatment is conducted by giving guidance on particularly important fields for a juvenile's rehabilitation, such as on his/her lifestyle, school life, employment, family relationships or friend relationships. Some assignments are given for him/her to perform, designed to help him/her solve their problems in such fields. b. Short-term probation for traffic offenses Short-term probation for traffic offenses is for a juvenile who is placed under probation by a family court order for traffic-related offenses as long as the juvenile does not have general delinquent tendencies or has not developed strong delinquent tendencies and his/her traffic-related delinquent tendencies are not fixed. This has been conducted since 1977, and 15,916 juveniles were newly placed under short-term probation for traffic offenses in 2005.
Short-term probation for traffic offenses lasts for a short period of three or four months in principle. Instead of ordinary treatment, group treatment concerning safe driving is conducted. (2) Characteristics of juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees a. Age Fig. 4-2-6-2 shows the age distribution of juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees newly placed under probationary supervision (excluding juveniles under short-term probation for traffic offenses; hereinafter the same in this Section) in 2005.
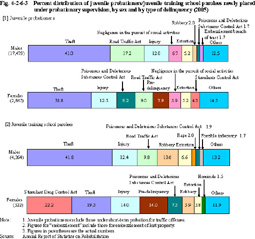
Fig. 4-2-6-2 Age distribution of juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees newly placed under probation (2005) b. Type of delinquency Fig. 4-2-6-3 shows the percent ratio of juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees newly placed under probationary supervision in 2005, by sex and by type of delinquency.
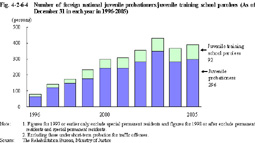
Fig. 4-2-6-3 Percent distribution of juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees newly placed under probationary supervision, by sex and by type of delinquency (2005) c. Nationality, etc. Fig. 4-2-6-4 shows the trends in the number of foreign national juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees (excluding permanent residents and special permanent residents; hereinafter the same in this Section) as of December 31 in each year, over the last 10 years.
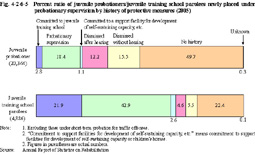
Fig. 4-2-6-4 Number of foreign national juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees (As of December 31 in each year in 1996-2005) As of December 31, 2005, the number of foreign national juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees was largest for Brazilian (201 juveniles in total), followed by Chinese (51 juveniles including Taiwanese), Filipino (41 juveniles), and Peruvian (40 juveniles).d. History of protective measures Fig. 4-2-6-5 shows percent ratio of juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees newly placed under probationary supervision in 2005, by history of protective measures.
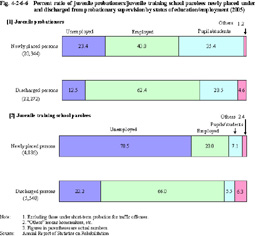
Fig. 4-2-6-5 Percent ratio of juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees newly placed under probationary supervision by history of protective measures (2005) e. Status of education or employment Fig. 4-2-6-6 shows the percent ratio of juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees newly placed under and discharged from probationary supervision (excluding those under short-term probation for traffic offenses; hereinafter the same in this Section) in 2005, by status of education or employment.
Fig. 4-2-6-6 Percent ratio of juvenile probationers/juvenile training school parolees newly placed under and discharged from probationary supervision by status of education/employment (2005) |