| Previous Next Index Image Index Year Selection | |
|
|
1. Basic systems for treatment The principles of treatment of inmates in penal institutions are placed on providing correctional treatment through the execution of their sentences and on their reform and social rehabilitation.There are two basic treatment systems:
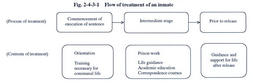
the Classified Treatment System, in which through scientific surveys to identify the problems of individual inmates,groups of inmates are organized and effective treatment is carried out in accordance with the nature of each group;and the Progressive Treatment System, in which four grades(Grades1to4)are established within the process of execution of an inmate's sentence,and an inmate progresses gradually from the bottom grade(Grade4)to higher grades,depending on his/her performance.Another type of treatment called Open Treatment is adopted,depending on the nature of inmates. Fig. 2-4-3- 1shows the flow of treatment of an inmate in a penal institution. Fig. 2-4-3-1 Flow of treatment of an inmate (1) Classified Treatment System The treatment of inmates in penal institutions aims at the correction of inmates for their smooth social rehabilitation.In order to achieve this,treatment is implemented in response to characteristics of individual inmates including the reasons for their committing offenses through scientific diagnosis of their personalities.Scientific surveys to identify the problems of individual inmates are called classifying examinations,and classification treatment includes preparing treatment plans based on these examinations results,organizing groups of inmates,and carrying out effective treatment for each group.
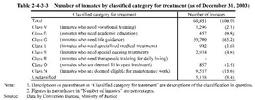
Classifying examinations are conducted as entry examinations within two months after an inmates imprisonment and as reexaminations(every two months for an inmate whose term of imprisonment is less than eight months and every six months for others,or occasionally as the need arises)on the basis of expertise and technology in medicine,psychology,education,sociology,and others.The result of classifying examinations is used for appropriate confinement and treatment,including determination of classified categories(for confinement and for treatment)and allocation of cells,decision of treatment guidelines for security,prison work,education program etc.,examinations for progressive treatment,and applications for parole. As one of the measures to improve the Classified Treatment System,special institutions(the Sapporo,Miyagi,Nagoya,Osaka,Hiroshima,Takamatsu and Fukuoka Prisons and the Kawagoe Juvenile Prison)are designated to carry out detailed examinations as a classification center in each of the Regional Correction Headquarters.Classification centers make the examinations of(i)newly imprisoned male inmates under16year of age whose term of imprisonment is three months or more and(ii)newly imprisoned male inmates16years and over but under28years of age,whose term of imprisonment is one year or more,and who have never been imprisoned before(excluding those clearly classified into Class F).Those classified into(i)are imprisoned in the Kawagoe Juvenile Prison. Based on the result of classifying examinations,a category for confinement(facility or division therein in which the offender is to be accommodated)and a category for treatment(prior policy of treatment for the inmate)are identified,and the facility for the inmate to be accommodated is then determined. Table 2-4-3-2 shows the number of inmates in each classified category for confinement as of December31,2003. Table 2-4-3-3 shows the number and the percentage of inmates in each classified treatment category as of December31,2003.Those inmates classified in Class G,who need living guidance,account for more than60%.There have been no changes in this trend in recent years. Table 2-4-3-2 Number of inmates by classified category for confinement(as of December31,2003) Table 2-4-3-3 Number of inmates by classified category for treatment(as of December31,2003) (2) Progressive Treatment System The Progressive Treatment System is a system in which four grades(Grades1to4)are created in the process of execution of the sentence and an inmate gradually progresses from the bottom grade(Grade4)to higher grades,depending on his/her performance.Accordingly,he/she is gradually given privileges and responsibilities in external communications etc.
The aim of the system is to encourage inmates to make voluntary efforts to reform themselves and improve their social aptitude. (3) Open Treatment System The Open Treatment System is a form of treatment for ensuring discipline through the inmate's responsibility and self-governing restrictions as a substitute for the use of locks and other physical facilities and equipment as well as supervision by staff to ensure confinement.It aims to provide effective treatment for social rehabilitation in an environment as similar to ordinary social life as possible,on the basis of trust in the inmate's self-discipline and sense of responsibility.It is mainly implemented in penal institutions housing traffic offenders.Open treatment is also implemented for non-traffic offenders as a developed form of outdoor work in locations such as Masukawa Farm attached to the Hakodate Juvenile Prison and the Oi Shipyard attached to the Matsuyama Prison.
In the institutions offering open treatment,cells,dining rooms,and workshops etc.are in principle kept unlocked.Life guidance,vocational training,and educational treatment necessary for inmates'social rehabilitation are provided in a relatively open environment. |